Confocal A1R HD 25

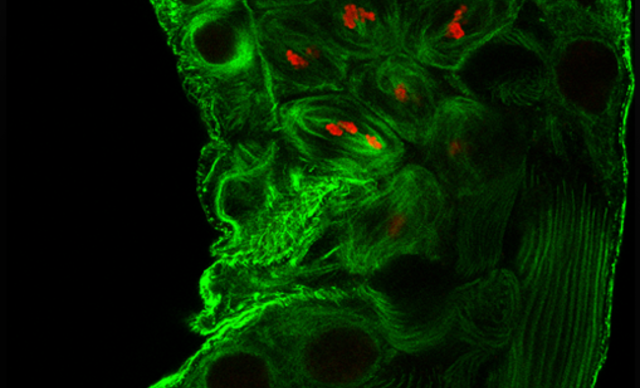
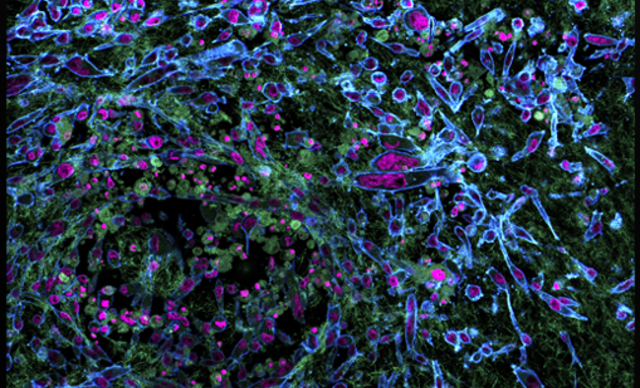
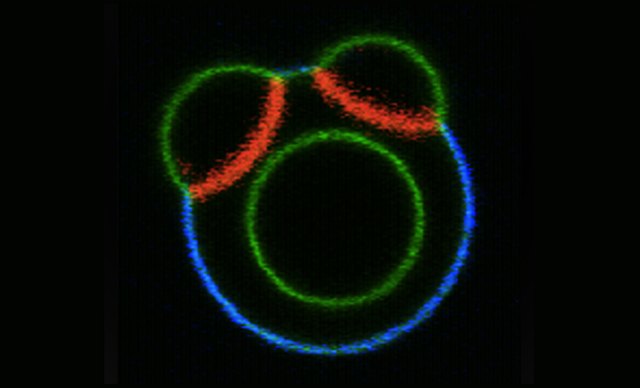
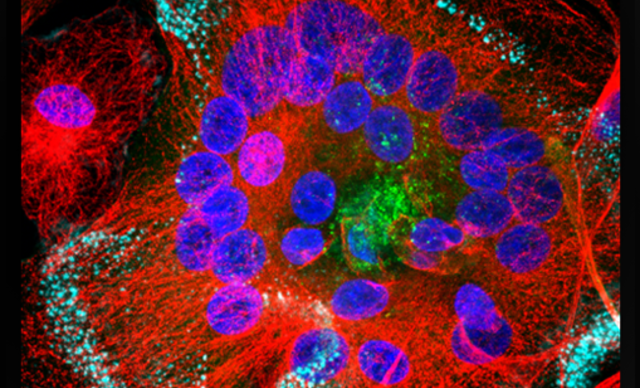
In the biomedical sciences, a major application of confocal microscopy involves imaging either fixed or living cells, and tissues that have usually been labelled with one or more fluorescent probes. A confocal microscope can capture images with a 25 mm field of view, nearly twice the area of conventional point scanners.
Capturing images of large samples such as tissues, organs and live model organisms, requires the detectable area of cellular response to be extended/enlarge and increasing the image capture speed.T he A1 HD25/A1R HD25 confocal microscope has the largest field of view (25 mm) in such microscopes, enabling users to expand the limits of scientific research.
Principle
Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy
Laser scanning confocal microscopes employ a pair of pinhole apertures to limit the specimen focal plane to a confined volume approximately a micron in size. Relatively thick specimens can be imaged in successive volumes by acquiring a series of sections along the optical (z) axis of the microscope.
The confocal Z-Axis Position and widefield Focus sliders are locked together at the same focal plane. They can be uncoupled with the Focus Lock checkbox for observation of a single focal plane in one window while the other is translated through successive view fields along the microscope optical axis. Use either the Z-Axis Position or Focus sliders to scan through successive focal planes, which will produce thin optical sections of the specimen in the confocal image window, and a succession of blurred images in the widefield image window. More...
Configuration
Illumination
-
LU-N4/N4S 4-laser unit 405 nm, 488 nm, 561 nm,640 nm lasers are installed; built-in AOTF
- Sola SM II : 5 solid-state sources operating simultaneously to produce white light, 380-680 nm.
Detectors
Confocal and Spectral detection in galvano and resonant mode :
- Standard fluorescence detector :A1-DUG-2 GaAsP Multi Detector Unit: 2 GaAsP PMTs + 2 Multi-Alkali PMTs
- Spectral detector : A1-DUS spectral detector unit, number of channels: 32
Objectives
Using silicone oil, which has a refractive index close to that of live cells, as the immersion liquid, permits high resolution imaging of thick samples as well as long-term time-lapse imaging, with a chromatic aberration correction from visible to UV and a nano crystal coat applied.
|
Magnification |
Type |
Immersion |
N.A |
WD |
|
|
Apo Lambda S |
Sil |
1.05 |
0.55 |
DIC |
|
|
Apo Lambda S |
Sil |
1.25 |
0.3 |
DIC |
|
|
Apo Lambda S |
Sil |
1.35 |
0.31-0.28 |
DIC |
Filters
|
Name |
EX |
DM |
EM |
|
UVA |
340-380 |
400 |
435-485 |
|
GFP |
465-495 |
505 |
515-555 |
|
TxRed |
540-80 |
595 |
600-660 |
|
G2A |
535-50 |
575 |
580 |
Associated Devices
- MCL 500µm Piezo stage
- ThermoBox and Stage heater controller, TokaiHit Co.
Techniques
- Epi-fluorescence
- Laser Scan Microscopy (LSM)
- Förster Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
- Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP)
- Reflectance
Applications
- Tissue, Organoids, Spheroids
- Fixed and Lived samples